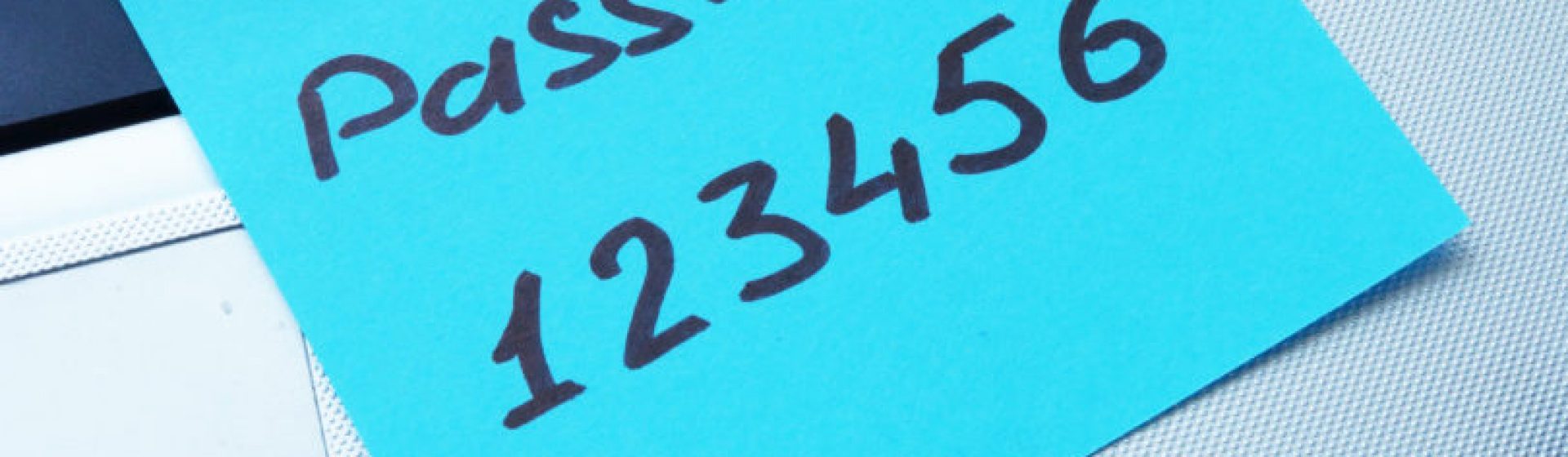2019 started with the largest data leak in the Internet history: over 700 million emails and more than 20 million passwords were compromised. The 87GB database containing usernames and passwords was circulating throughout the Internet.
This was the security researcher, Troy Hunt, who discovered the largest data dump known as Collection #1. It was posted on the MEGA cloud storage service. Hunt noted that before the file was deleted, the data had been burnt across the hacker forums.
Although it’s hard to identify where the files originated from, the expert assumes that this is the result of a number of individual breaches, which were combined in a single database. While most of the email credentials were compromised earlier with some of them dating back to 2008, around 140 million email addresses didn’t appear in previous breaches and are newly exposed data. It implies either the recent unreported large breach or many small breaches.
To get access to various user accounts, hackers use the credential stuffing approach – they enter the exposed usernames and passwords on the scope of platforms. This technique is successful because people tend to reuse passwords for their multiple accounts.
Top 5 mistakes every person makes when managing passwords
Password Reuse
People use the same password across various platforms at an alarmingly high rate despite the warnings by the IT community. Today people have a plethora of accounts at different websites. As a result, they need to keep in mind the login details for all those accounts. According to the study, 52% of the surveyed come up with the solution of reusing the same or similar password. While this practice can put at risk all accounts at once, the issue with reusing passwords for professional services becomes even more burning because it endangers the company’s sensitive data.
Recently, the attackers have used a list of passwords stolen from the third party services and tried to get access to the TurboTax return information including social security numbers, names, and addresses. They have succeeded with only one account though.
What’s worse, the users are reluctant to update their credentials even after the breach. Over 70% of people continue to use a compromised password up to a year, and 40% up to 3 years after the incident.
Poor authentication methods
People neglect additional account security measures like two-factor authentication. Even the strongest password is hackable, unfortunately. The password is only one layer of your account protection; 2FA gives an additional layer of security and reduces the risks of a hack.
As the name implies, this method requires two ways of identification. Just like a website asks to confirm your email address, 2FA asks to confirm your identity. The authentication factors can be your biometric data, one-time password sent via SMS to your smartphone, or an answer to the security question. You should add 2FA to accounts with your personal and financial data like email, banking, payment and e-shopping accounts.
Saved credentials
People allow their browsers to remember their login details. The browsers helpfully offer to save your login credentials and take away the burden of typing them each time you want to access one of your accounts. It’s easy and convenient, as you don’t need to remember different passwords for different services – but it exposes your sensitive data to risk.
If your device is lost or stolen; or hackers get remote access to your computer over the Internet, they will exploit all the account credentials you store in the browser.
Weak passwords
Despite the numerous breaches and data leaks, the “123456” password is still the most popular. Yeah, right!
Any data connected to your personality such as the names of your family members or pets, birthdays, social security numbers, addresses is easy to compromise, as well as dictionary words and commonly used phrases. These weak passwords can be cracked within seconds.
Not updated passwords
You might be surprised, but most people update their login details only when the situation forces them. Generally, users do it when they forget passwords or are required by the system. In fact, the LastPass research shows that 39% of those surveyed never change their password if it’s not required.
Regular or frequent password updates improve security and eliminate the use of saved passwords. By this, you invalidate the compromised credentials if someone gets access to them without your knowledge. The benefit of this strategy is worth the inconvenience it brings with creating a strong password regularly and remembering it.
What are the best security practices?
The above mentioned bad habits are the main causes of cybersecurity breaches. The attackers are aware of these mistakes and take full advantage of them. It is critical to educate the employees and individuals on the password hygiene and its importance. The password security methods available today can make it extremely hard for attackers to get your credentials.
Passphrase
Passphrase is a sentence or a series of words that is used instead of a password for authentication. It’s more complex and longer than a password, and thus more secure. The passphrases are easier to remember, and are hard or even impossible to crack because most cracking tools are usually capable of breaking only ten-character passwords.
In order to enhance the passphrase, use both capital and low-case letters, symbols, special characters, etc. Make sure you don’t employ popular quotes that are easy to guess.
Multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication is a combination of two or more factors for authorization. Utilizing different categories of factors (i.e. what the user knows, has and is) like biometrics, one-time password, phone call, email, PIN code compensates for the weakness of each factor. Most breaches could be prevented due to this additional layer.
MFA is an effective protection method since the hacker can’t have access to all the factors needed to verify your identity. Companies that employ MFA have more credibility and trustworthiness in the users’ eyes.
Managing tools
Password manager is a software application that allows you to store and manage your numerous passwords. The program also generates long and complex passwords which you don’t need to come up with on your own. It’s a secure ‘registry’ for all your login credentials locked in an encrypted vault. You do have to create and remember a unique and strong master password to get access to the rest of your passwords. Of course, don’t reuse it anywhere.
Hardware storage
Hardware-based password security system is a physical unit that ensures secure storage of your passwords. Since the password is still a dominant form of authentication, the cybersecurity teams do their best to develop appropriate storage solutions.
The critical steps in the sphere have already been taken by Authentico Technologies. They have come up with a risk-free solution for managing and storing passwords within the enterprise. Authentico Technologies offer a hardware unit that utilizes the PUF (physically unclonable function) technology. The device processes the salted password hashes and stores the output. To check the validity PUF compares the output with the corresponding stored value. It means that offline password recovery is impossible, and the information won’t be compromised even if the database is hacked.
A final word
In the digital era, people entrust many aspects of their lives to the Internet and storage devices. Thus, cyber hygiene is a protective routine that will keep your sensitive information secure. It’s imperative to employ cybersecurity practices and turn them in everyday habits.
With the ubiquitous use of technology, average employees are responsible for maintaining security just as IT teams are. The awareness among individuals of potential threats and measures capable to prevent them is a must. Practicing elementary rules of cyber hygiene like using strong passwords for different accounts, encryption of information, regular updating of software will eliminate and mitigate the cyber threats.